In a historic achievement for the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO), the Aditya satellite has successfully reached the Sun’s L1 point, approximately 1.5 million kilometers from Earth. The mission, which began on September 2nd last year, aimed to position India’s Aditya satellite at the Earth-Sun L1 point, enabling continuous observation of the Sun and studying solar activities.
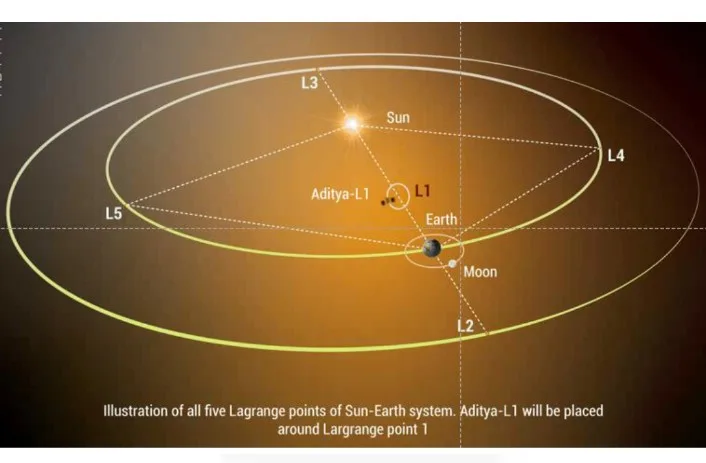
Aditya-L1, now established in its designated orbit, offers a unique vantage point to observe solar phenomena and study their effects on space weather. The L1 point provides an unobstructed view of the Sun from all directions in the heliosphere.
Prime Minister Narendra Modi congratulated ISRO on this remarkable achievement. He commended the dedication of Indian scientists and their relentless pursuit of scientific advancements, emphasizing the mission’s significance in expanding our understanding of solar activities.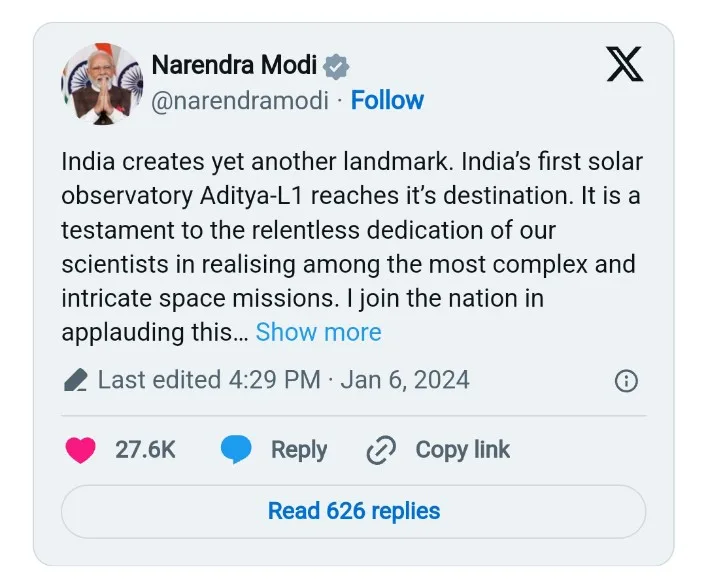
Aditya-L1 Mission Success: A Milestone in Space Exploration
The successful execution of the Aditya-L1 mission marks a significant achievement for ISRO and the Indian scientific community. The mission’s objective is to explore the mysteries of the Sun-Earth connection and unravel the complexities of solar phenomena.
Central Minister Jitendra Singh also took to social media to express his excitement, highlighting the remarkable milestones achieved by India in space exploration this year. From Moon missions to solar dances, Singh praised the visionary leadership of PM Modi and termed the Aditya-L1 mission as another success story written under his guidance.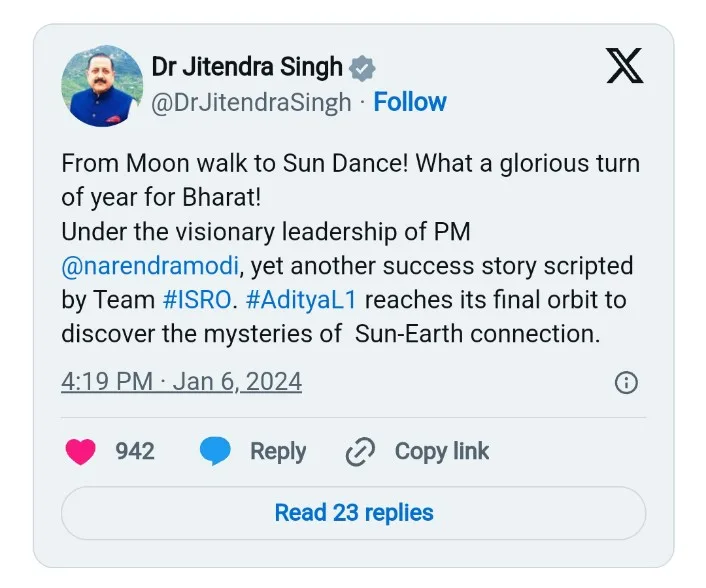
Understanding Lagrange Point 1 (L1)
The Aditya satellite has positioned itself near the Lagrange Point 1 (L1), situated about 1.5 million kilometers away from the Earth-Sun system. L1 is a unique region where gravitational forces between Earth and the Sun are balanced, allowing for a stable position. The satellite’s presence at L1 enhances its ability to continuously observe the Sun and monitor solar activities.
Last year in September, ISRO’s Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV-C57) successfully launched the Aditya-L1 mission, setting the stage for a groundbreaking exploration of the Sun’s mysteries. The mission aims to study the solar atmosphere, the Sun’s corona, solar flares, and their impact on space weather.
As India revels in this achievement, the Aditya-L1 mission promises to open new frontiers in solar research and contribute valuable insights to the global scientific community.